SKUs were first introduced in the 1930s by supermarkets looking to streamline their warehouse management processes. Today, SKUs are used across a wide range of industries, including retail, manufacturing, and eCommerce. Let’s see how you can implement SKUs in your business.
What Does SKU Stand For?
What does SKU mean for a marketplace? The SKU acronym stands for Stock Keeping Unit. It is a unique identifier assigned to a product by a vendor, distributor or manufacturer for inventory tracking purposes. A SKU typically consists of a combination of numbers and letters that identify the product’s characteristics, such as color, size, style, and packaging.
SKU codes can be used in various industries, including retail stores, eCommerce, and manufacturing to keep track of inventory levels, sales performance, pricing, and promotions.
Why Are Stock Keeping Units Important to Business
Stock Keeping Units are important to businesses for several reasons:
- Organization: SKUs help businesses organize their inventory by categorizing products based on various attributes such as size, color, material, etc. This helps in easy tracking, management, and retrieval of products.
- Efficiency: SKUs allow businesses to track inventory and stock levels accurately, thereby reducing the cost of overstocking or under stocking of products. This, in turn, leads to better management of resources and helps organizations optimize their business processes.
- Sales analysis: With SKUs, businesses can track the sales of individual products and analyze the performance of various product categories. This analysis can help businesses make data-driven decisions about product inventory, promotions, and pricing strategies.
- Customer service: SKUs allow businesses to quickly identify products and process orders, which improves the overall customer experience. This can help businesses build brand loyalty and increase customer retention.
Overall, SKUs are an important tool for businesses to manage their stocks, optimize operations, and improve their customer service.
How to find SKU Number?
SKU numbers can be found in different places, depending on how the product is sold and marketed. Here are some common ways to find SKU numbers:
- Check the product packaging or label – Most products have a SKU number on their packaging or label. Look for a series of numbers and letters that is usually located near the barcode.
- Check the product listing online – If you’re buying a product online, the SKU number may be listed in the product description or specifications.
- Check the purchase receipt – The SKU number may be listed on the purchase receipt or invoice.
- Look at the product catalog – If you’re a business owner, the SKU numbers for your products may be listed in your product catalog.
Parts of SKU Number
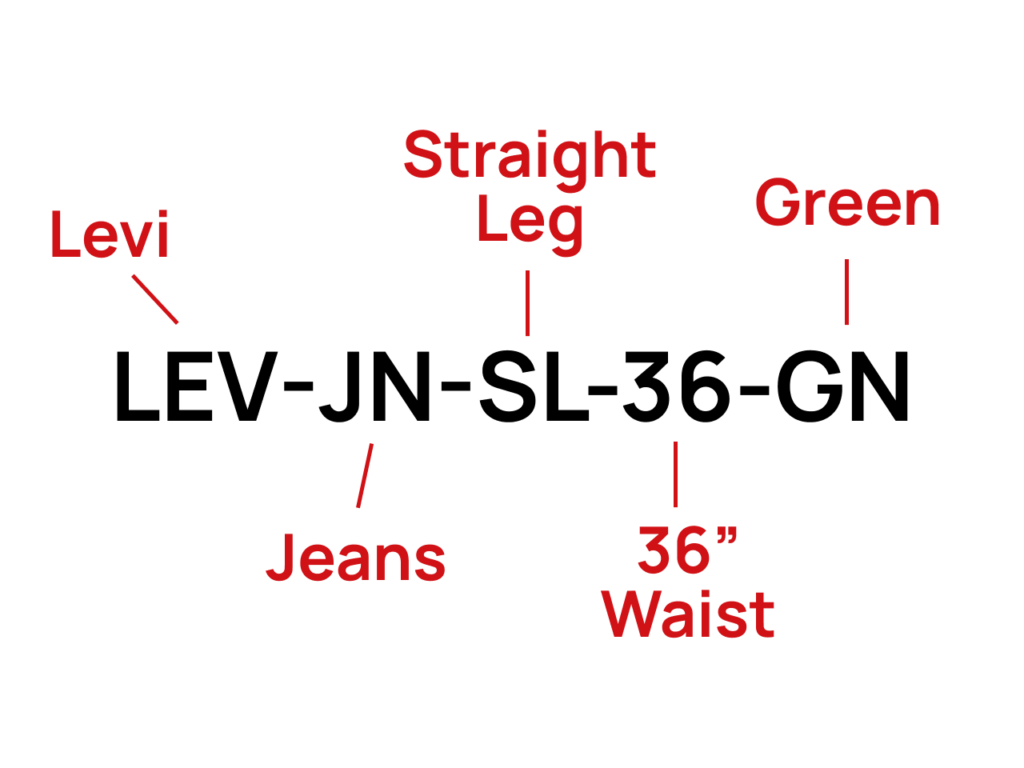
SKU numbers are made up of a combination of letters and numbers, and each digit or letter can represent specific information about the product, such as its size, color, manufacturer, or price.
For example, the SKU number of a Levi’s pair of green jeans with straight leg and 36’’ may be something like LEV-JN-SL-36-GN. The SKU number helps distinguish this particular product from other jeans in different colors or sizes, making it easier to manage inventory and sales data.
Or WJ-1234-M-RED. In this example, WJ represents the brand, 1234 is the product code, M stands for medium size, and RED is the color.
SKU vs UPC
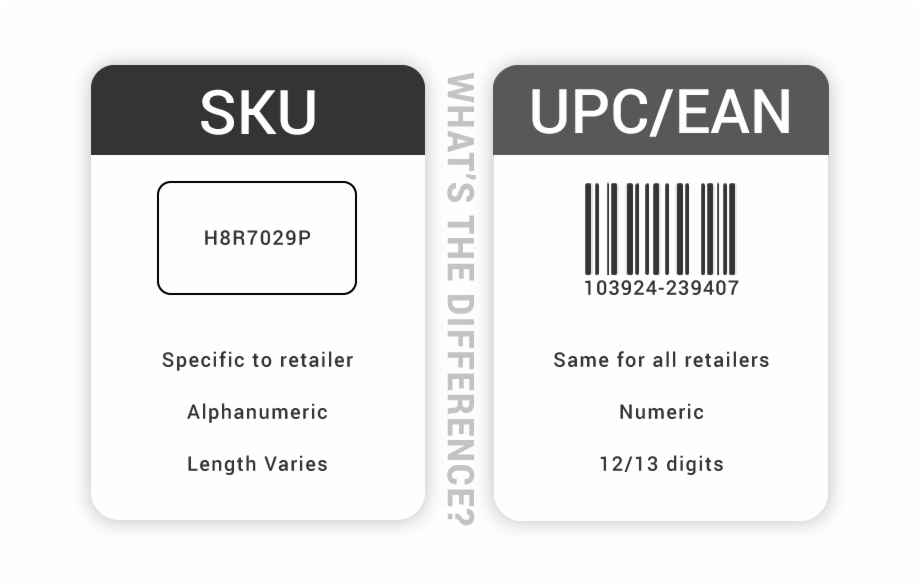
The Stock Keeping Unit and UPC (Universal Product Code) are both codes used in retail to identify products to track stocks, sales, and pricing.
Product SKUs are unique alphanumeric codes used by a retailer to identify and differentiate products. They are created by retailers to help manage their inventory and track sales. Each product has a unique SKU, which typically includes information such as the brand, style, color, and size.
UPC, on the other hand, is a standardized barcode system used to identify products globally. It is assigned by the manufacturer and includes a 12-digit number that represents the product and its features. UPC codes are used to scan products at the point of sale, track items, and improve supply chain management.
While both SKU and UPC are used for inventory tracking, they serve different purposes. SKU in retail can be used to track their internal inventory and sales, while UPC codes are applied by manufacturers to track products in the supply chain.
SKU vs Serial Numbers
SKU is a unique code assigned to each product with the company’s nomenclature. It is used to track the item’s stock level, price, and other details related to inventory management. SKU codes are usually alphanumeric and can be customized by the company.
A serial number, on the other hand, is a unique identifier assigned to each individual item within a specific product line. It is used to track the item’s history, warranty, and other details related to the product’s manufacturing and distribution. Serial numbers are usually numeric and are assigned by the manufacturer.
SKU vs Barcode vs Part Number
SKU, Barcode, and Part Number are all codes used in inventory management to identify products.
SKU is a unique identifier assigned by a retailer to a specific product. It is used to track stock unit levels and sales.
Barcode is a series of lines and spaces that represent a product’s unique identifier. It can be scanned using a barcode scanner to quickly and accurately identify the product.
Part Number is a unique identifier assigned by a manufacturer to a specific product. It is used to track inventory levels and production.
In summary, SKU is used by retailers, barcode is used for scanning, and part number is used by manufacturers.
SKUs and POS Systems
SKUs are unique identification codes used to track and manage stock. Each product has its own SKU assigned to it, which helps in managing and simplifies the process of ordering and stocking products.
POS (Point of Sale) systems, on the other hand, are software and hardware systems used at checkout to process transactions, manage inventory, and generate reports.
SKUs and POS systems work together to provide retailers with accurate and timely sales data to make informed business decisions.
Best Practices for Generating SKUs
Here are the best practices for generating SKUs that may apply in many different situations:
- Keep it concise and meaningful: A good SKU is usually a combination of letters and numbers that make sense within the context of the product it represents. It should be short enough to be easily remembered and written down, but long enough to be unique.
- Use a consistent format: Your SKUs should follow a consistent format across your entire inventory. This will make it easier to sort, search and retrieve products when needed.
- Avoid using special characters and spaces: Special characters and spaces can cause issues when importing or exporting data, or when trying to search for products in a database.
- Ensure uniqueness: Each SKU should be unique for each product in your inventory to avoid duplicates, overlaps, or confusion.
- Length: The length of the SKU should be kept between 6 and 10 characters.
- Be specific: Use descriptive words in the SKU to make it easier to identify the product.
- Avoid repetition: Don’t repeat letters or numbers in the SKU.
- Plan for future growth: Consider the scalability of your SKU system as your business grows.
Here are some examples of the best SKU formats:
- A combination of letters and numbers (e.g., ABC123)
- A sequential numbering system (e.g., 00001, 00002, 00003)
- A product code based on categories and subcategories (e.g., WD01 or FNS001)
SKU Examples
Let’s see some examples of SKUs:
- Nike Air Jordan’s shoes: AJ1234-567 (a SKU containing letters and numbers)
- Apple iPhone 12 Pro: A14-BLK-256GB (a SKU that includes model name, color, and storage capacity)
- Walmart’s Great Value Canned Corn: 12345 (a simple SKU that is just a number)
- SKU for a Shopify item could be “SHOES-001” for a pair of shoes, where “SHOES” represents the category and “001” represents a unique identifier for that specific product.
- A seller might assign the SKU “FBM001” to a pair of shoes they’re selling on Facebook Marketplace. They can then use this SKU to easily track how many pairs of shoes they have in stock, which ones have sold, and which ones are still available for sale.
SKU Customization
Customizing SKUs can also help businesses distinguish between similar products or track products with different attributes (such as size or color).

Some ideas for SKU customization include:
- Using a combination of letters and numbers to create a unique code for each product. For example, a t-shirt could have the SKU “TS01BLK” (for black) or “TS02RED” (for red).
- Including attributes in the SKU code, such as size, material, or product type. For example, a dress could have the SKU “DR01MLVS” (for a medium-sized, sleeveless dress).
- Using sequential numbers as part of the SKU code to indicate when a product was added to inventory. For example, a new t-shirt could have the SKU “TS2021001” (indicating it was added to inventory in 2021).
Overall, the goal of SKU customization is to create a system that is easy to use and understand for both businesses and customers.
How to Create SKU Numbers
There are several tools available that can be used to create SKUs, such as:
- SKU Labs – a software solution that automates inventory, order, and shipping management. It also includes a feature to create custom SKUs for products.
- Zoho Inventory – an SKU management software that comes with a SKU generator feature. This tool can help create custom SKUs for products and variants.
- QuickBooks – an accounting software that also includes an inventory management feature. It allows users to create custom SKUs for products.
- Trade Gecko – a management software that offers various features to manage products, orders, and finances. It also includes a SKU generator tool.
If you run a CS-Cart based store, SKU can be added to your products when you create them or can be imported in bulk with the help of a CSV file. When opting to integrate either of the above systems for SKU adding, feel free to contact us. We have experience in integration of SKU-systems.
Conclusion
By customizing the SKU codes, eCommerce stores can organize their stock keeping better, make it easier for customers to search for products, and track sales and items more effectively.
Some eCommerce platforms such as CS-Cart offer SKU customization options built-in. However, if you are using a custom-built eCommerce store, you may need to hire a developer to help you with SKU customization.
Overall, SKU eCommerce site customization is a common practice for eCommerce stores that can help streamline inventory management and improve customer experience.
SKU numbers FAQ
Can SKUs be customized?
Yes, SKUs can be customized to meet the needs of individual businesses. Some companies might use a different numbering system or add additional information to their SKUs for easy tracking.
How do I create SKUs for my products?
To create SKUs for your products, you’ll need to decide on a numbering system and then assign unique codes to each item. Other important factors to consider include product categories, variants, and attributes.
How to create an SKU in CS-Cart?
Follow these steps:
– Log in to your CS-Cart account.
– Go to the Products section and click on Add Product.
– Fill in the necessary details, such as the product name, price, and description.
– Under the General section, you will see an option for SKU. Input your unique SKU code here, which should consist of a combination of letters, numbers, and/or symbols.
– Save the product, and your SKU will be created.
What is the role of SKU in supply chain management?
It helps to identify and track products throughout the supply chain, from manufacturing to sales, and plays a crucial role in managing inventory levels, forecasting demand, and improving operational efficiency.
Some of the key benefits of using SKU in supply chain management include:
– Accurate tracking of inventory levels and movements
– Effective demand forecasting and planning
– Streamlined logistics and order fulfillment
– Improved customer satisfaction and retention
Why is SKU crucial for logistics?
Each SKU represents a specific product variant, allowing logistics teams to identify items quickly and accurately, track stock levels, and minimize inventory carrying costs.
What is SKU for manufacturing?
The SKU helps the manufacturer to manage and track its inventory, as well as to analyze its sales performance. By assigning a unique SKU to each product, the manufacturer can easily identify and manage its stock levels, reorder products when needed, and avoid overstocking or under stocking.
What is the role of SKU in marketing?
The primary role of SKU in marketing includes:
– Inventory management: SKU helps businesses to effectively track and manage their inventory levels. By assigning unique codes to products, businesses can easily monitor which products are selling and which ones are not.
– Pricing strategy: Businesses can use SKU to apply different pricing strategies for the same product, based on its variations. For example, a product in different colors can have different prices.
– Marketing strategy: SKU helps businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns for specific products. By analyzing the sales data of each SKU, companies can create marketing plans that are tailored to each product’s unique features and customer needs.
What does SKU mean for management?
By using SKUs, businesses can identify which products are performing well and which ones are not, helping them to make data-driven decisions about pricing, promotions, and product development.
What is multi SKU?
Multi SKU refers to a product that has multiple variations or options, such as different colors, sizes, or features. Each variation is assigned a unique SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) to help manage inventory and track sales. For example, a shirt that comes in three different colors and four different sizes would have 12 different SKUs.
What are SKU tags used for?
SKU tags are used to track inventory levels, sales, and reorder quantities. They are also used for marketing purposes, as they can be used to identify products in advertising and promotional materials.
